Description
 The parasitic jaeger is 21
inches in length with a wingspan of
36
inches. It has a hooked bill, webbed feet, a white patch on the underside of its wings, and
pointed central tail feathers that stick out beyond its other tail feathers. During the non-breeding season, it looses its central tail feathers. Males and females look alike. The parasitic jaeger is 21
inches in length with a wingspan of
36
inches. It has a hooked bill, webbed feet, a white patch on the underside of its wings, and
pointed central tail feathers that stick out beyond its other tail feathers. During the non-breeding season, it looses its central tail feathers. Males and females look alike.
The parasitic jaeger has two different color patterns or morphs. Morphs are variations in a bird species' plumage. In its light morph, it
is brown on its uppersides, dark brown on the cap of its head, light yellow-brown on its neck and throat, and white on its belly. It may also have a full or partial gray-brown band across its breast. In its dark morph, it is brown on its head and undersides.
Range 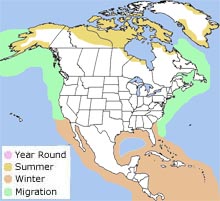 The parasitic jaeger is found in northern Alaska and northern Canada during the breeding season. During migration, it is found
on shores and estuaries.
It winters
on offshore waters south to South America. It is also found in northern Europe and Asia. The parasitic jaeger is found in northern Alaska and northern Canada during the breeding season. During migration, it is found
on shores and estuaries.
It winters
on offshore waters south to South America. It is also found in northern Europe and Asia.
|
|
Habitat
The parasitic jaeger breeds on the tundra and coastal marshes in the Arctic. In the winter, it usually is found on the open ocean close to the shoreline.
Diet
 The parasitic jaeger is a very fast and agile flier. It uses its flying skills to get food! The parasitic jaeger waits for a gull or a tern to catch a fish. It then quickly swoops in and chases the other bird until it drops its catch! The parasitic jaeger then swoops down and snatches up the dropped prey!
This is called
kleptoparasitism and it is where the parasitic jaeger gets its name. It also forages on the ground for food and will eat insects, berries, small mammals, bird eggs, and young birds. The parasitic jaeger is a very fast and agile flier. It uses its flying skills to get food! The parasitic jaeger waits for a gull or a tern to catch a fish. It then quickly swoops in and chases the other bird until it drops its catch! The parasitic jaeger then swoops down and snatches up the dropped prey!
This is called
kleptoparasitism and it is where the parasitic jaeger gets its name. It also forages on the ground for food and will eat insects, berries, small mammals, bird eggs, and young birds.
Life Cycle
 The parasitic jaeger nests in colonies. The male chooses a nesting site and the female builds the nest. The nest is a shallow depression in the ground or in rocks. The nest is usually lined with grass, moss, or lichen. The female lays 2 eggs and both the male and female incubate the eggs for 26-28 days. Both parents feed and care for the chicks. The chicks leave the nest a few days after hatching, but they continue to be fed and cared for by their parents until they fledge when they are 25-30 days old. The parasitic jaeger nests in colonies. The male chooses a nesting site and the female builds the nest. The nest is a shallow depression in the ground or in rocks. The nest is usually lined with grass, moss, or lichen. The female lays 2 eggs and both the male and female incubate the eggs for 26-28 days. Both parents feed and care for the chicks. The chicks leave the nest a few days after hatching, but they continue to be fed and cared for by their parents until they fledge when they are 25-30 days old.
Behavior The parasitic jaeger aggressively protects its nesting territory and flies at and pecks the head of intruders. The
parasitic jaeger is also sometimes known as the arctic skua or the arctic jaeger.
|



 The parasitic jaeger is found in northern Alaska and northern Canada during the breeding season. During migration, it is found
on shores and
The parasitic jaeger is found in northern Alaska and northern Canada during the breeding season. During migration, it is found
on shores and 
