Description
 The great blue heron is the largest heron in North America. It stands three to four feet tall and has a wingspan of almost six feet. It has blue-gray feathers on most of its body and a plume of feathers on its chest and back. The great blue heron is the largest heron in North America. It stands three to four feet tall and has a wingspan of almost six feet. It has blue-gray feathers on most of its body and a plume of feathers on its chest and back.
It has long legs with rusty-red thighs and a long, straight, dagger-like yellowish bill that turns orange at the beginning of the breeding season. Adults have white on the top of their heads and long black plumes above their eyes.
There is an all white version of the great blue heron that is found in the Florida Keys. It is sometimes known as the great white heron, but it is simply a white version of the great blue heron.
Range
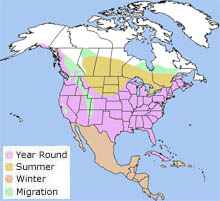 The great blue heron breeds from Canada south to the Caribbean and Mexico. It winters as far north as southern Alaska and New England. It is also found in the Galapagos Islands.
The great blue heron is found in New Hampshire. The great blue heron breeds from Canada south to the Caribbean and Mexico. It winters as far north as southern Alaska and New England. It is also found in the Galapagos Islands.
The great blue heron is found in New Hampshire.
HabitatThe great blue heron is found in marshes, rivers, lakes, salt water shores, and ponds. | |
Diet  The great blue heron hunts for food during the day and at night. It stands in the water and waits for prey like frogs and fish to pass by and then grabs them with its long bill. It also eats salamanders, lizards, snakes, shrimps, crabs, crayfish, dragonflies, grasshoppers, aquatic insects, and occasionally birds and small mammals like mice. The great blue heron hunts for food during the day and at night. It stands in the water and waits for prey like frogs and fish to pass by and then grabs them with its long bill. It also eats salamanders, lizards, snakes, shrimps, crabs, crayfish, dragonflies, grasshoppers, aquatic insects, and occasionally birds and small mammals like mice.
Life Cycle
 The female great blue heron lays 3-7 eggs on a shallow platform made of sticks and twigs and lined with soft material. The nest is usually in a tall tree, but it may be built in the reeds or on a cliff edge. The eggs hatch in about a month and the chicks fledge when they are about two months old. Great blue herons nest in colonies. They usually nest in the same spot from year-to-year. They may even use the same nest. The female great blue heron lays 3-7 eggs on a shallow platform made of sticks and twigs and lined with soft material. The nest is usually in a tall tree, but it may be built in the reeds or on a cliff edge. The eggs hatch in about a month and the chicks fledge when they are about two months old. Great blue herons nest in colonies. They usually nest in the same spot from year-to-year. They may even use the same nest.
Behavior  The great blue heron migrates in the fall, although some populations in the southern part of their range stay where they are. The great blue heron usually tucks its head into an S-shape when it is resting and flying. The great blue heron migrates in the fall, although some populations in the southern part of their range stay where they are. The great blue heron usually tucks its head into an S-shape when it is resting and flying.
|



 The great blue heron breeds from Canada south to the Caribbean and Mexico. It winters as far north as southern Alaska and New England. It is also found in the Galapagos Islands.
The great blue heron is found in New Hampshire.
The great blue heron breeds from Canada south to the Caribbean and Mexico. It winters as far north as southern Alaska and New England. It is also found in the Galapagos Islands.
The great blue heron is found in New Hampshire.

